Aluminium’s dynamic trajectory
Aluminium is no longer just a versatile metal—it’s the foundation for a changing industrial world. The 2025 outlook suggests a year where every tonne of aluminium used carries not only value but also consequence. From downstream products to recycling systems, this metal’s journey reveals much about sustainability, innovation, and economic ambition.
Downstream: The pulse of aluminium progress
The downstream aluminium segment is a true engine room of global manufacturing. It converts raw aluminium into usable forms—flat rolled products (FRP), extrusions, foil, castings, and wire rods—each powering different industries.
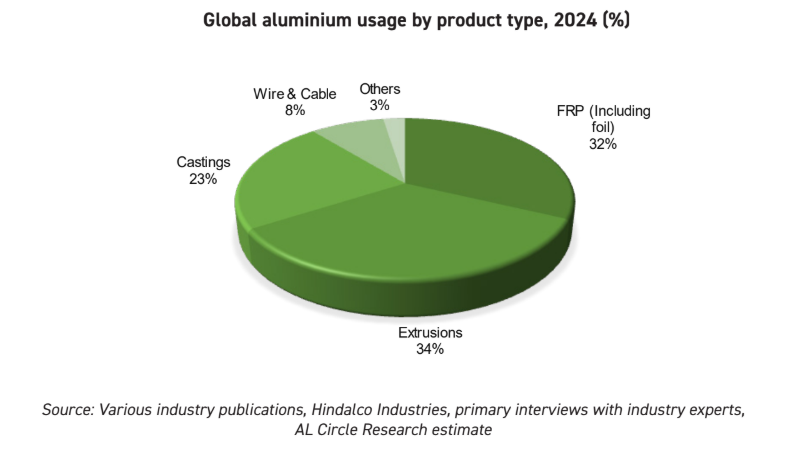
In 2024, global usage of aluminium was led by extrusions 34%, followed closely by FRP, including foil 32%. Castings took 23%, wire rods 8%, and niche applications consumed the rest. These percentages are more than statistics—they are blueprints of tomorrow’s global economy.
FRP: From beverages to buildings
FRP consumption fell by 4% in 2023. Yet 2025’s outlook remains optimistic. Lightweight yet durable, FRPs continue to be used in aircraft, construction, and electric systems. China dominates this sector—both in production capacity and export momentum.
Extrusions: Engineering flexibility
Extrusions shape skylines, solar frames, car chassis, data centre cooling structures, etc. Their dominance stems from adaptability. Usage forecasts suggest significant growth in Asia-Pacific, thanks to infrastructure build-outs and lightweight trends in auto manufacturing.
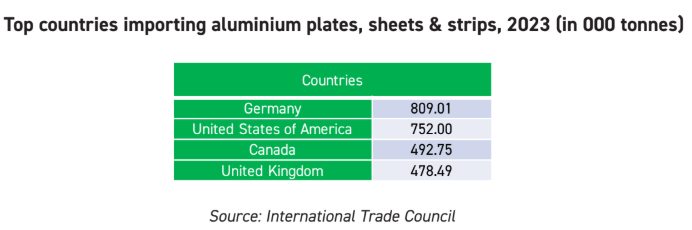
Global aluminium extrusion usage by region, 2024(in million tonnes)
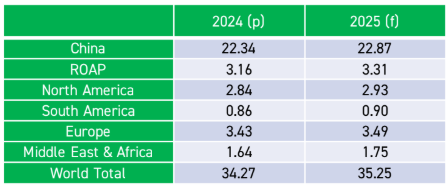
Source: AL Circle Research Estimate
Foil: Lightness that packs power
Foil plays a silent yet vital role. It wraps medicines, seals freshness, and conducts energy. This thin material carries hefty expectations, with packaging firms switching to aluminium for sustainability. Between 2024 and 2025, usage is forecast to recover steadily.
Wire rods: Conducting the energy future
Wire rods feed directly into the veins of renewable energy. Global usage was about 7.9 million tonnes in 2023, heading toward 10.1 million tonnes by 2030. Aluminium’s place in modern power systems is not just growing—it’s surging.
Castings: Mobility’s essential form
In the form of wheels, frames, engine housings—castings are vital to mobility. Demand from electric vehicle (EV) makers remains robust, especially as weight reduction drives efficiency. Growth will be supported by investments in die-casting upgrades across Asia.
End-use sectors: Where aluminium comes alive
Aluminium reaches its full potential in real-world applications. By 2025, consumption patterns are set to evolve in response to industrial shifts, policy changes, and consumer preferences.
Transportation: Full throttle ahead
From EVs to aircraft, rails to ships—transport continues to drive aluminium usage. Aluminium content in EVs has already tripled since 2015. By 2030, EV-linked demand alone could reach 10 million tonnes globally.
The advantages are tangible—recyclability, weight reduction, and crashworthiness. With EV sales expected to hit nearly 45 million units by 2030, aluminium will ride that wave at full speed.
Construction: Building smart, building light
Construction work is forecast to exceed $13.9 trillion by 2037. Aluminium contributes via window frames, façades, curtain walls, and electrical wiring. India, China, U.S. are at the forefront of this growth.
Urbanisation is pushing aluminium usage up. Modular, energy-efficient buildings are demanding aluminium components with both aesthetic appeal and performance.
Packaging: Lightweight, infinite
Aluminium packaging is more than cans. It’s preservation. It’s brand value. It’s a circular economy in action. Beverage cans usage will continue growing at 4.09% CAGR through 2030.
Recyclability is the big story. Seventy-five per cent of all aluminium ever made is still in use. That’s more than an environmental stat—it’s proof of concept.
Electric Systems: Connecting the future
As nations build smarter grids, aluminium wire rods are indispensable. Whether in power lines, transformers, battery cables/battery terminals—demand surges alongside renewable capacity.
Solar PV systems are aluminium-intensive. Frames, racking structures, and connectors all rely on aluminium’s conductivity, corrosion resistance, and structural integrity.
Electronics: Quiet power
Laptops, heat sinks, smartphones, LEDs—all owe performance to aluminium. As miniaturisation continues, thermally conductive yet lightweight metals like aluminium take center stage.
Recycling: The circular reinvention
Recycling is no longer an option—it’s a mandate. By 2025, global recycled aluminium production and usage is expected to rise sharply, driven by climate policy, consumer sentiment, and cost efficiency.
Volume, momentum, value
Between 2023 and 2025, global recycled aluminium usage is forecast to grow consistently. Europe remains a global leader, with over 60% of aluminium produced via recycling. In automotive and construction, recycling rates exceed 90%.
Post-consumer scrap availability is rising, and trade in recycled aluminium is shifting. Developing nations, especially in Southeast Asia, are fast becoming import destinations.
Competitive advantage
Producing recycled aluminium requires only 5% of the energy used for primary production. This economic leverage is now turning into an ESG advantage. From beverage can makers to car manufacturers—green aluminium is shaping brand value.
Innovation in process
Technological advancements in recycling are reshaping capacity. Smelters now adopt AI-driven scrap sorters, dross recyclers, and closed-loop systems. Inert anode smelting and hydrogen-based refining may soon define the low-carbon frontier.
Aluminium’s sustainability renaissance
Net-zero goals are not theoretical anymore—they are strategic priorities. Aluminium, as a metal that enables decarbonisation across industries, is at the heart of the transition.
Industry giants like Alcoa, Hydro, Vedanta, Rio Tinto have all pledged deep emission cuts by 2030, with roadmaps to net zero by 2050. From solar-powered smelters to closed-loop recycling plants—green infrastructure is being laid down globally.
New aluminium products are being introduced with low-carbon labels—Hydro CIRCAL, EGA’s CelestiAL, Alcoa’s EcoLum, Vedanta’s Restora—all catering to buyers who care about footprints, not just price points.
The market dynamics: Growth with caution
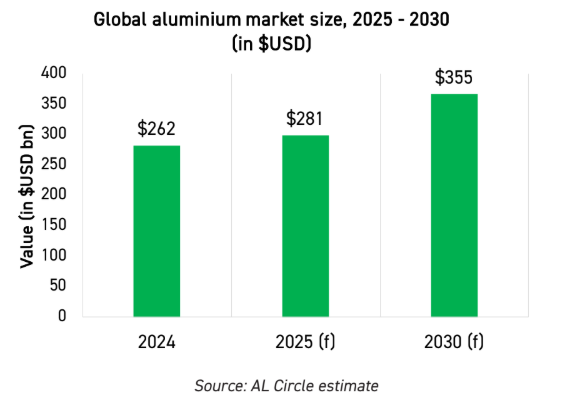
By 2025, the global aluminium market is projected to hit $355 billion. Growth rates average 4.8% CAGR through 2030. Yet this story isn’t without hurdles.
Interest rate volatility, energy shocks, geopolitical events, raw material constraints—all cast shadows. Yet the resilience of aluminium lies in its versatility. It moves with demand patterns and reinvents itself with each innovation.
Policy, investment, trade
Regulatory clarity will be crucial. Governments now reward green sourcing through tariffs, incentives, and ESG-linked financing. Supply chains must adapt to traceability mandates and carbon disclosure norms.
Investment is flowing into both greenfield (new recycling plants) and brownfield upgrades (refining retrofits). Trade policies—especially around scrap movement—are under review across multiple jurisdictions.
China, Europe, India, and the U.S.—each is calibrating import-export dynamics with their net-zero roadmaps.
The AL Circle Lens: Why this report matters
The 2025 AL Circle outlook isn’t just data—it’s an invitation. It calls producers, recyclers, consumers, and regulators to rethink aluminium’s role in global systems. It spotlights signals of change and maps how aluminium can thrive in a carbon-constrained future.
It’s more than an industry forecast—it’s a vision for responsible growth.
Our take: Prepare for the aluminium economy
The new aluminium economy is circular, digital, policy-sensitive, and customer-led. Whether you are investing in extrusion plants or looking at scrap trading opportunities, 2025 is the time to reposition. Subscribe to read the report today!
As stakeholders prepare for the year ahead, this message rings clear: aluminium is more than material—it is strategy, sustainability, and system.














