The global aluminium industry operates as a vast and intricate ecosystem, where even the smallest regulatory adjustments can set off chain reactions that ripple throughout the entire value chain. Governments hold considerable sway over the industry’s trajectory, from energy policies to trade tariffs.
Any such decision made by governments can send shockwaves that reverberate among aluminium producers and consumers globally, reshaping supply chains and influencing investment decisions. In this in-depth analysis, we’ll explore the turbulent landscape of regulations and tariffs that affect the global aluminium market, examining their various impacts on the relevant stakeholders and uncovering the emerging trends guiding the market’s future.
US tariffs and the European Union’s environmental initiative: A complex trade tale
The United States’ imposition of tariffs, mainly targeting China, reshaped global trade dynamics overnight. Despite the intention to shield domestic producers, these tariffs had far-reaching consequences, leading to price hikes that undermined the competitiveness of downstream industries.
Simultaneously, the European Union embarked on an initiative to promote sustainability within the aluminium industry. The EU aimed to incentivise environmentally friendly practices by introducing carbon taxes on aluminium imports.
However, this initiative posed challenges for countries heavily reliant on coal-based energy, such as India, where increased export costs strained the industry. In contrast, nations like Norway, with robust emission trading systems and green energy infrastructure, were better equipped to navigate these regulatory challenges.
China’s export tax policy and its global reach
As the heavyweight in the aluminium market, China often finds itself at the centre of policy debates. With a history of utilising export taxes to fuel domestic growth, China’s moves have significant ramifications on the global stage.
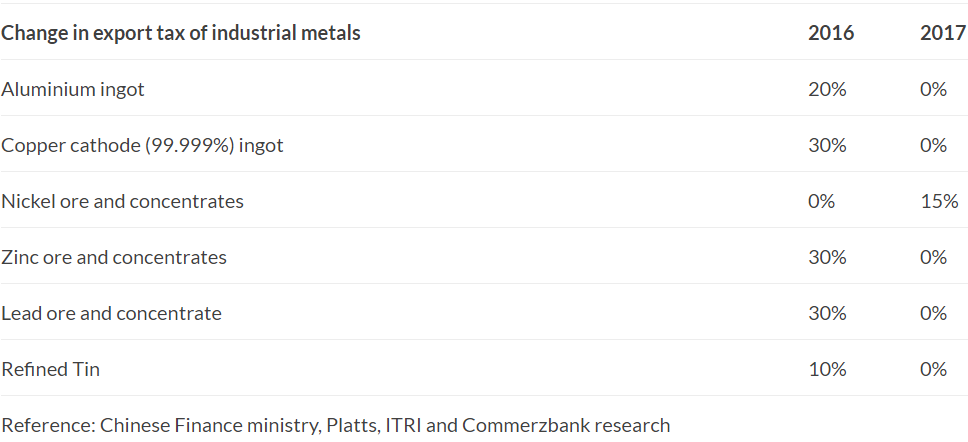
In 2017, the Chinese government adjusted the export tax on all major industrial metals. With few exceptions, the tax was significantly reduced or completely abolished.
However, the unintended consequence was a flood of surplus aluminium in the global market as downstream producers reaped the benefits of reduced costs.
As the Chinese economy slowed, oversupply became a pressing issue, prompting China to temporarily lift export taxes. While attempting to alleviate domestic oversupply, this move inadvertently worsened the global surplus, driving prices even lower. It vividly illustrates how decisions made within one country can send shockwaves across the global aluminium market.
India’s high tariffs: Striking a balance
In India, high tariffs on aluminium products aim to protect domestic producers but inadvertently stifle downstream industries. These measures create a delicate balance, a tightrope walk, between protectionism and competitiveness.
Much like the situation in the United States, while these tariffs may shield primary aluminium producers, they can hinder downstream manufacturers in sectors such as electronics and automobiles. Furthermore, they limit access to recycled aluminium and scrap materials, exacerbating challenges for industries reliant on these resources.
Geopolitical tensions and their global impact
Geopolitical tensions, such as those between Russia and Western nations, have massive implications for the aluminium industry. Tariffs and sanctions imposed in response to such tensions disrupt supply chains and reshape markets instantly.
For example, following Ukraine-related tensions, the United States slapped a 200% tariff on Russian aluminium imports, severely impacting the Russian aluminium industry. This event underscores the industry’s vulnerability to geopolitical shifts and the urgent need for implementing robust risk mitigation strategies. The geopolitical crisis led to soaring energy costs in the European Union, particularly affecting aluminium production in countries like Germany.
The global aluminium industry is intricately tied to a complex web of government regulations and tariffs, with each policy decision carrying profound implications for stakeholders. From China’s export tax policies to the EU’s environmental initiatives, the regulatory landscape changes weekly, presenting challenges and opportunities for industry players.
Successfully navigating this terrain demands foresight, adaptability, and a deep understanding of global market dynamics. As demand for aluminium rises, industry stakeholders must remain vigilant and agile to thrive in an ever-changing regulatory environment.